Solvent
Extraction Method of Edible Oil Using Hexane
Introduction
The solvent extraction method is
one of the most widely used industrial processes for producing edible oils from
oilseeds such as soybean, sunflower, groundnut, rice bran,
cottonseed, mustard, and corn germ.
This method is especially preferred when the oil content of seeds is low or
when maximum oil recovery is required.
Among various solvents, hexane is
the most commonly used solvent in the edible oil industry due to its high oil
solubility, low boiling point, easy recovery, and cost-effectiveness.
Why Hexane Is Used as a Solvent
Hexane is a petroleum-derived organic solvent that has
ideal properties for oil extraction:
· Excellent
solubility for vegetable oils
· Low
boiling point (~65–70°C), making recovery easy
· Chemically
stable and non-reactive with oil
· High
extraction efficiency (up to 98–99%)
· Economical
and reusable after recovery
Because of these advantages, food-grade
hexane is widely accepted in edible oil processing plants
worldwide.
Raw Materials Used
Solvent extraction is mainly used for:
· Soybean
· Rice
bran
· Sunflower
seed
· Cottonseed
· Mustard
seed
· Groundnut
cake (after expelling)
· Corn
germ
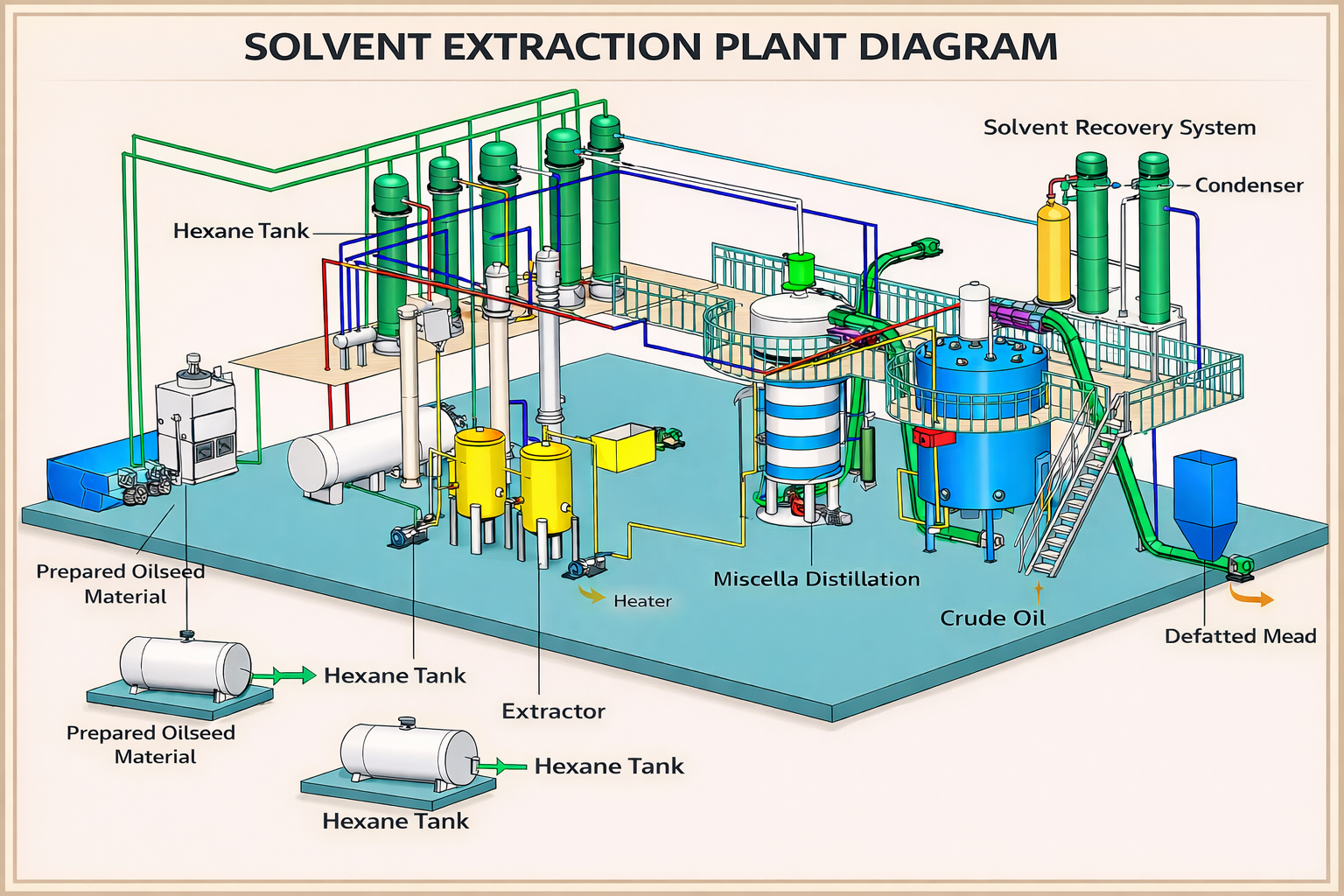
Step-by-Step Solvent Extraction
Process
1. Seed Preparation
Oilseeds are first cleaned to remove dust, stones, metal
particles, and foreign matter.
Then they undergo:
· Dehulling (removal
of husk, if required)
· Crushing
or flaking to increase surface area
· Conditioning by
heating to optimize oil release
Proper preparation ensures efficient solvent penetration.
2. Extraction with Hexane
Prepared flakes or cake are fed into the extractor.
· Hexane
is sprayed or percolated through the material
· Oil
dissolves into hexane, forming a mixture called miscella (oil
+ hexane)
· The
remaining solid material becomes defatted meal
At this stage:
· Oil
recovery can reach 98–99%
· Minimal
oil remains in the meal
3. Miscella Distillation (Oil
Recovery)
The miscella is heated in distillation
units:
· Hexane
evaporates at low temperature
· Oil
is separated and collected
· Evaporated
hexane is condensed and reused
The recovered oil at this stage is called crude oil.
4. Desolventizing of Meal
The defatted meal still contains traces of hexane.
· Meal
is sent to a Desolventizer-Toaster (DT)
· Steam
and heat remove remaining hexane
· Hexane
vapors are recovered and reused
The final meal is:
· Safe
for animal feed or food applications
· High
in protein (especially soybean meal)
5. Solvent Recovery System
To ensure safety and economy:
· All
hexane vapors are condensed
· Recovered
hexane is recycled back into the system
· Losses
are kept extremely low
Modern plants achieve over 99.5% solvent recovery.
Post-Extraction Refining of Oil
The crude oil obtained by solvent extraction is not directly
edible.
It undergoes refining steps such as:
1.
Degumming –
Removal of phospholipids
2.
Neutralization –
Removal of free fatty acids
3.
Bleaching –
Removal of color pigments
4.
Deodorization –
Removal of odor and taste
After refining, the oil becomes Refined,
Bleached, and Deodorized (RBD) edible oil, suitable for human
consumption.
Advantages of Solvent Extraction
Method
· Very
high oil recovery (maximum yield)
· Economical
for large-scale production
· Suitable
for low-oil-content seeds
· Produces
high-protein defatted meal
· Continuous
and automated process
Safety and Environmental
Considerations
Hexane is flammable, so modern plants include:
· Explosion-proof
equipment
· Vapor-tight
systems
· Fire
detection and suppression
· Strict
monitoring of solvent losses
Food-grade hexane residues in oil are removed completely
during refining, making the final oil safe for consumption as
per international standards.
Conclusion
The solvent extraction method using hexane is
a highly efficient, proven, and globally accepted technology for edible oil
production.
It ensures maximum oil recovery, consistent quality, and economic viability,
especially for large-scale edible oil plants.
With advanced solvent recovery and refining systems, this
method plays a crucial role in meeting the growing global demand for
high-quality edible oils.